Summary: As AI, cloud platforms, and connected devices are increasingly used in pharmaceutical systems, validation has become even more important. This blog looks at the role of Computer System Validation (CSV) in regulated environments.
New technologies are changing how Computer System Validation (CSV) is handled in practice. As AI, cloud platforms, blockchain, and connected devices are introduced into business systems, older validation approaches are often not enough on their own. These technologies bring operational benefits, but they also change how systems behave, which has to be considered during validation.
In pharmaceutical and healthcare settings, computer system validation is required to support data integrity and accountability. Within the computer system validation in the pharmaceutical industry, growing system connectivity and closer regulatory oversight are increasing reliance on structured computer system validation services. This shift is also shaping how AI is applied in computer system validation, especially as digital systems become more interconnected.
Market Size and Growth Projections:
Regional Insights of Computer System Validation in Pharmaceutical industry:
- North America: Dominates the CSV market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global share in 2022.
- Europe: Holds 25% of the market share, with countries like Germany, France, and the U.K. being key contributors.
- Asia Pacific: Accounts for approximately 15% of the market share, with significant growth observed in countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
The upward trajectory of the CSV market underscores its critical role in ensuring compliance and operational excellence within the pharmaceutical industry.
Key Growth Drivers for CSV:
Below are a few factors that are driving the demand for advanced CSV processes.

The Development of CSV: From Conventional to Advanced Technology
Earlier CSV practices were built around manual testing and extensive documentation. These methods were manageable when systems were smaller and less connected. As environments became more complex, the effort required to maintain validation increased, along with the compliance workload.
Automation and integrated platforms later changed how validation activities were performed. FDA guidance on Computer Software Assurance (CSA) reflected this shift by focusing on risk, intended use, and practical testing. Less emphasis was placed on document volume and more on evidence of control, data integrity, and system reliability.
Emerging Technologies Driving Change in CSV
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
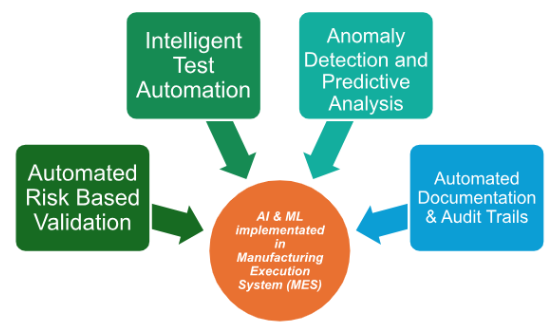
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are now used in different parts of pharmaceutical research, development, and manufacturing. The examples below show how these technologies are applied in practice.
- Sanofi: Partnered with AI platform company Aily Labs to develop "plai," an AII application that aggregates internal data to support decision-making across drug development processes.
- Pfizer: Collaborated with IBM's supercomputing and AI technologies to accelerate drug discovery, notably in the development of PAXLOVID, an oral COVID-19 treatment.
- Novartis: Engaged in partnerships with Microsoft and NVIDIA to integrate AI into over 150 ongoing projects, aiming to improve drug discovery and operational efficiency.
2. Cloud Computing
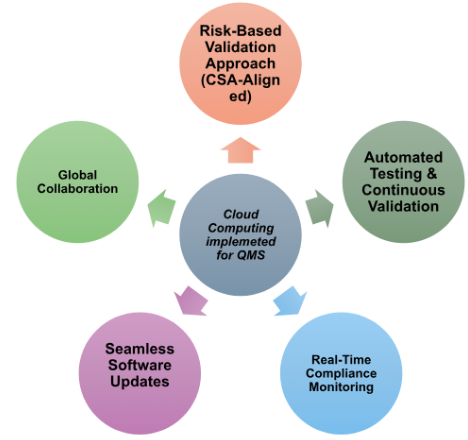
Cloud computing is another technology being adopted in the pharmaceutical industry to enhance operations and drive innovation. Some of the companies include:
- AstraZeneca: Collaborated with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to process vast genomics data, enabling the execution of 51 billion statistical tests in under 24 hours, thereby accelerating drug discovery.
- Pfizer: Partnered with AWS to leverage machine learning and cloud computing, streamlining drug discovery and development processes.
- Novartis: Teamed up with Microsoft Azure to utilize AI for modeling and predicting drug interactions, expediting the formulation process and fostering global collaboration among researchers.
- Sanofi: Invested significantly in cloud computing through partnerships with key vendors to enhance data analytics capabilities and operational efficiency.
3. Blockchain
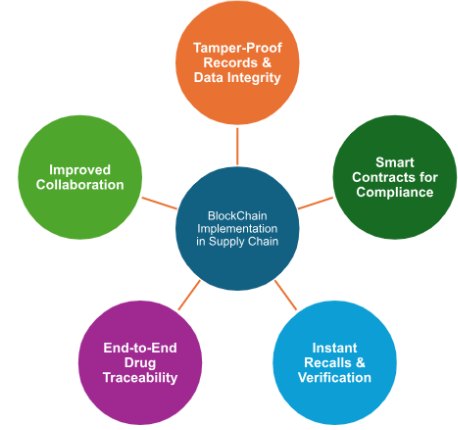
Pharmaceutical companies have also implemented blockchain technology to enhance the security and transparency of their supply chains. This can be seen in:
- Merck KGaA: Utilizes blockchain to combat counterfeit drugs by creating a transparent tracking system. Each transaction, from production to sale, is recorded on the blockchain, allowing for the verification of a drug's authenticity at every stage.
- IBM's Collaboration with Pharmaceutical Companies: To develop a blockchain-based platform that provides end-to-end visibility across the drug supply chain. This initiative aims to reduce the risk of counterfeit medications and ensure regulatory compliance.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
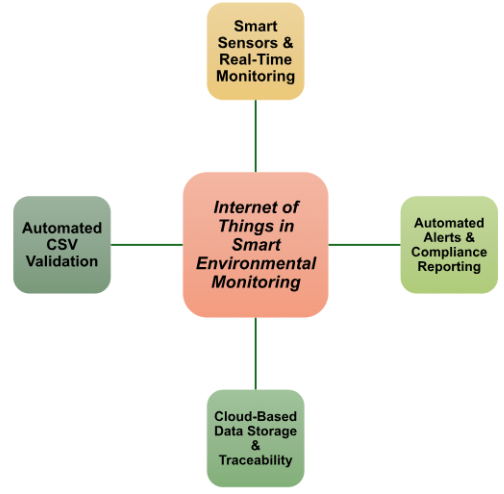
IoT technologies are used in different parts of pharmaceutical operations, particularly where monitoring, traceability, and real-time data are required.
- Pfizer and Moderna: Utilized IoT sensors during the COVID-19 pandemic to monitor the storage and transportation conditions of vaccines, ensuring they remained within required ultra-cold temperature ranges to maintain efficacy.
- Novartis: Partnered with Qualcomm to develop IoT-enabled smart inhalers that track patient usage, providing real-time data to improve patient adherence and treatment outcomes.
- AstraZeneca: Uses IoT devices in its manufacturing environments to monitor production conditions during drug manufacturing.
- Johnson & Johnson: Implemented IoT solutions to optimize their supply chain logistics, using connected devices to track the location and condition of pharmaceutical products during transit, ensuring product integrity and timely delivery.
5. Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Automation and Robotic Process Automation are used in different parts of pharmaceutical operations, including regulatory, manufacturing, and laboratory areas. The examples below reflect current usage.
- GlaxoSmithKline (GSK): GSK uses cloud-based workflow tools to support regulatory operations across regions. Platforms such as Smartsheet are used to manage submissions, track tasks, and improve coordination across teams involved in regulatory filings.
- Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS): Bristol Myers Squibb applies automation in parts of its cell therapy manufacturing process. Through collaborations with companies such as Cellares, the focus is on automating specific production steps to support consistency and scale in complex therapies.
- Opentrons: Opentrons develops laboratory automation systems used to run and scale experimental workflows. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these systems were used to increase testing throughput by automating repetitive laboratory tasks.
Challenges and Considerations for CSV in the Age of Emerging Technologies
While emerging technologies offer significant benefits, they also present unique challenges for CSV. Some of these include:

The Future of CSV in the Digital Age
As AI-enabled systems, cloud platforms, IoT devices, and automated workflows become more common, CSV will continue to evolve. Validation activities are likely to place greater emphasis on automation, ongoing monitoring, and targeted testing rather than one-time execution.
Organizations will need to invest in updated tools and skills while aligning validation practices with both current regulations and emerging guidance to excel.
Conclusion
CSV today looks very different from what it did even a few years ago. It now has to account for AI-enabled features, cloud-based platforms, connected devices, and workflows that change more frequently than before. As a result, validation teams are being pushed to move away from document-heavy legacy approaches and toward methods that are risk-based, scalable, and aligned with FDA CSA guidance.
Jade Global works with life sciences and healthcare organizations to modernize Computer System Validation and Computer Software Assurance in ways that reflect how regulated systems are designed, integrated, and maintained today. Our team brings practical experience across GxP validation, enterprise quality engineering, and regulated application testing, while staying closely aligned with FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GxP, and GMP requirements. We support validation across complex, interconnected environments spanning Oracle, SAP, Salesforce, Boomi, Veeva Vault, and TrackWise, with a consistent focus on data integrity and audit readiness as systems continue to evolve.
Using an automation-led Testing as a Service model, and supported by partnerships with AWS, Tricentis, and Atlassian, we help QA teams spend less time on repetitive manual work, move through validation cycles more efficiently, and lay the foundation for continuous, intelligence-driven compliance in digital-first operations.
Discover Jade’s CSV and CSA capabilities. Talk to our experts to learn more.













